-
 Phytochrome
Phytochrome
-
 Heat transfer fluid
Heat transfer fluid
-
 Offspring
Offspring
-
 GMO
GMO
-
 Iridescence
Iridescence
-
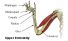 Humerus
Humerus
-
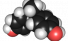 Bisphenol A
Bisphenol A
-
 Ria
Ria
-
 Electrophoresis
Electrophoresis
-
 Rectrice
Rectrice
-
 Ramjet engine
Ramjet engine
-
 Quantum number
Quantum number
-
 Class II antiarrhythmics
Class II antiarrhythmics
-
 GMT
GMT
-
 Serotonin
Serotonin
-
 Pacific rosewood
Pacific rosewood
-
 IATA
IATA
-
 Deep convection
Deep convection
-
 Apoplexy
Apoplexy
-
 Hijacker
Hijacker
-
 Random number
Random number
-
 Vega
Vega
-
 Solar sail
Solar sail
-
 Downy oak
Downy oak
-
 Hormone therapy
Hormone therapy
-
 Xylene
Xylene
-
 Infuse
Infuse
-
 Diplodocus
Diplodocus
-
 Watt-hour
Watt-hour
-
 Damselfly
Damselfly
Catalase
Structure of catalase
Catalases are found in all aerobic organisms, in the peroxisomes of eukaryotes. They are enzymes formed from four peptide chains, each composed of over 500 amino acids. They contain iron atoms within hemes, which are the active sites of the protein.
The function of catalase
The oxygen-oxygen bond of hydrogen peroxide is broken by the iron in the heme group, creating a molecule of water and a highly oxidising iron-oxygen bond. This can oxidise a new molecule of hydrogen peroxide giving dioxygen. The enzyme reaction involved is one of the fastest known.
Within the cell, the catalase protects the organism from the harmful oxidising action of hydrogen peroxide.
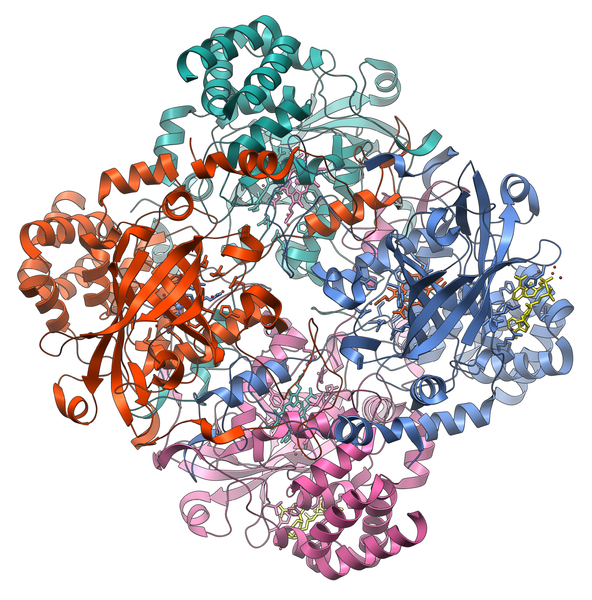 Catalase is an enzyme with four sub-units. © Vossman, Wikimedia, CC by-sa 3.0
Catalase is an enzyme with four sub-units. © Vossman, Wikimedia, CC by-sa 3.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



