-
 Liver
Liver
-
 Nymphosis
Nymphosis
-
 ISRO
ISRO
-
 Necrosis
Necrosis
-
 Quicklime
Quicklime
-
 CAIB
CAIB
-
 Encoder
Encoder
-
 Albuginea
Albuginea
-
 Contraception
Contraception
-
 Cement
Cement
-
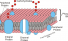 Glycocalyx
Glycocalyx
-
 Morbidity
Morbidity
-
 Photoelectric
Photoelectric
-
 Neoplasm
Neoplasm
-
 HDCP
HDCP
-
 Tidal Gate
Tidal Gate
-
 In vitro fertilisation
In vitro fertilisation
-
 Whiskers
Whiskers
-
 Organiser
Organiser
-
 Smog
Smog
-
 Beta version
Beta version
-
 Acoustic crest
Acoustic crest
-
 Immunity
Immunity
-
 VDSL 2
VDSL 2
-
 Directivity
Directivity
-
 Sea ice - First year thick
Sea ice - First year thick
-
 Lagooning
Lagooning
-
 Newton
Newton
-
 Sulforaphane
Sulforaphane
-
 Technical assessment
Technical assessment
Sweet chestnut
The sweet chestnut is a majestic tree that grows to a large size, it can reach heights of 30 metres.
Names
The sweet chestnut (Castanea sativa), a member of the Fagaceae family, was called the "acorn of Zeus" by the Greeks.

Castanea sativa. © FIR0002, GNU Free Documentation License version 1.2
Botanical description
The rectilinear trunk of the sweet chestnut is covered with dark brown bark which cracks lengthwise. Its deciduous leaves are alternate, about twenty centimetres long, petiolate, tough and feature large pointy teeth. In autumn, this foliage turns a pretty yellow colour which quickly changes to brown. Much like the oak and the beech, two trees from the same family, the leaves of the sweet chestnut remain on the tree for part of the winter. This plant only flowers after about twenty years, in the summer, producing male flowers in raised yellow 10-15 centimetre catkins and small female flowers, at the base of the catkins. Its fruit are burrs covered with many supple prickles and contain two or three chestnuts.
Origins
The botanical name of the sweet chestnut, "castanea", comes from Castanis, an ancient city located in present-day Turkey. Originally from Asia Minor, this fruit tree was introduced into the Cévennes region in France by the Romans.
Growing conditions
This species grows in full light or partial shade, although young plants prefer the shade. It does not tolerate extreme, cold or calcareous soil. It grows well in poor, acidic or sandy soil. It thrives in the Brittany and Massif Central regions of France, but is also found in many other regions, especially the Parisian basin.

Castanea sativa. © MPF, GNU Free Documentation License version 1.2
Use
The fruit of this tree, chestnuts, are edible and used in recipes for delicious dishes. In the past, chestnuts were a food staple in rural areas, particularly during the winter. Sweet chestnut wood is waterproof and elastic and is used to produce poles, parquet floors, barrels as well as chip board, paper pulp and furniture.
Author: Michel Caron
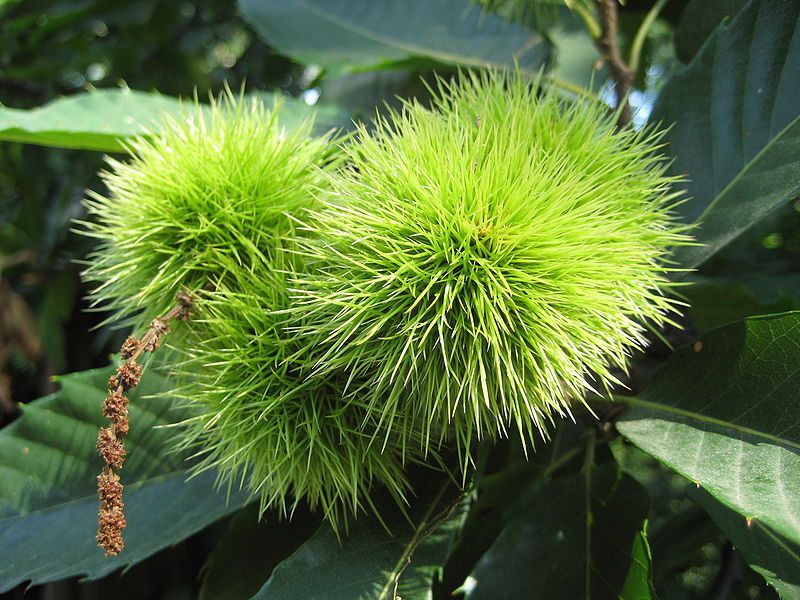 Castanea sativa. © Aconcagua, GNU Free Documentation License version 1.2
Castanea sativa. © Aconcagua, GNU Free Documentation License version 1.2
Latest
Fill out my online form.



