-
 Rosacea
Rosacea
-
 RSPB
RSPB
-
 Fibrin
Fibrin
-
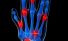 Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy
-
 Shiga toxin
Shiga toxin
-
 Histone
Histone
-
 Red panda
Red panda
-
 Aristotle's lantern
Aristotle's lantern
-
 Marsis radar
Marsis radar
-
 Terra
Terra
-
 Pruritus
Pruritus
-
 Taxonomy
Taxonomy
-
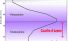 Ozone layer
Ozone layer
-
 IPv4
IPv4
-
 Launcher Integration Building
Launcher Integration Building
-
 Pigment
Pigment
-
 Flex fuel
Flex fuel
-
 McNaught's comet
McNaught's comet
-
 Ariane 5
Ariane 5
-
 Visual pollution
Visual pollution
-
 Barycentric
Barycentric
-
 Vacuum permeability
Vacuum permeability
-
 Caustic
Caustic
-
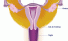 Cervix
Cervix
-
 GSS-API
GSS-API
-
 Polarisation
Polarisation
-
 Clay
Clay
-
 Essential amino acids
Essential amino acids
-
 Marburg fever
Marburg fever
-
 Interstellar dust
Interstellar dust
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is an energetic biochemical reaction that takes place inside plants.
Role of photosynthesis
The purpose of photosynthesis is to create energy (in the form of carbohydrates) from luminous energy produced by the sun. Organisms that use the mechanism of photosynthesis are autotrophic, because they produce organic matter from inorganic matter.
Mechanism of photosynthesis
Solar energy is used to oxidise water and reduce carbon dioxide in order to synthesise organic substances (carbohydrates). This phenomenon takes place in chloroplasts, an organelle specific to plants, around the thylakoid membranes where photosystems I and II and cytochromes are located.
Energy produced by photosynthesis
It takes six molecules of carbon dioxide and six molecules of water to synthesise one molecule of glucose, releasing six molecules of dioxygen, with the help of luminous energy.
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + luminous energy → C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6 O2
This process of production is broken down into two successive steps:
- photochemical reactions (light phase) : 12 H2O + light → 6 O2 + chemical energy (24 H) ;
- Calvin cycle (dark phase) : 6 CO2 + chemical energy (24 H) → C6H12O6 + 6 H2O.
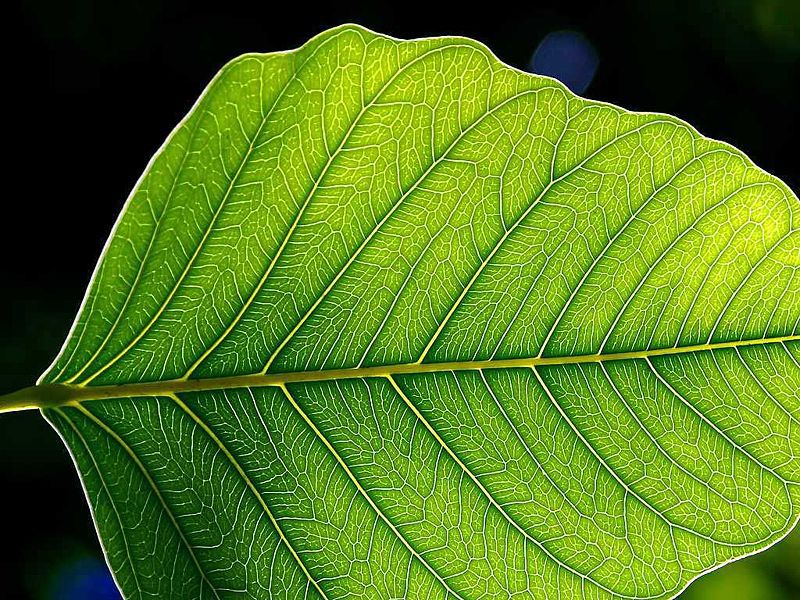 Photosynthesis is a mechanism specific to green plants. © Jon Sullivan, Wikimedia public domain
Photosynthesis is a mechanism specific to green plants. © Jon Sullivan, Wikimedia public domain
Latest
Fill out my online form.



