-
 Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis
-
 Morphing
Morphing
-
 Deletion
Deletion
-
 Gunning
Gunning
-
 Actin
Actin
-
 Schweizerhalle disaster
Schweizerhalle disaster
-
 Passphrase
Passphrase
-
 Pentose
Pentose
-
 Goniometer
Goniometer
-
 Gel
Gel
-
 OCO
OCO
-
 Handover
Handover
-
 Pyroxenite
Pyroxenite
-
 Relative permittivity
Relative permittivity
-
 Phobos
Phobos
-
 Thrust
Thrust
-
 Cremaster
Cremaster
-
 Electroencephalograph
Electroencephalograph
-
 IETF
IETF
-
 Exfoliation
Exfoliation
-
 API
API
-
 FSC
FSC
-
 Intrusion prevention system
Intrusion prevention system
-
 Oxidation zone
Oxidation zone
-
 Permian
Permian
-
 Cave pearls
Cave pearls
-
 Clay
Clay
-
 Rosemary
Rosemary
-
 Frequency band
Frequency band
-
 Caecum
Caecum
Handkerchief tree
The handkerchief tree is a species that can reach heights of 10 to 18 m and is remarkable by the originality of its structure, flowers and fruit.

Davidia involucrata. © Tim Waters, Flickr CC by nc-nd 2.0
Names
The handkerchief tree (Davidia involucrata), from the Nyssaceae family, takes its name from the very long white bracts that accompany its flowers.
Botanical description of the handkerchief tree
This tree has a conical then ovoid structure, often with several trunks. Its bark is brown and has delicate scales. Its deciduous oval and heart-shaped leaves at the base are similar to those of the linden tree. Dentate, they measure between 8 and 15 cm, they are dark green on top and pubescent and greyish on the underside.They turn yellow in autumn. It May its flowers, which are located at the end of a long peduncle, are yellow with reddish stamens grouped into knobs accompanied by large white 12 cm to 15 cm bracts. Its fruit look like small nuts.They are 3 cm wide and are brown when ripe.

Fruit of the handkerchief tree. © douneika, Flickr CC by nc sa 2.0
Origins
The handkerchief tree, originally from China, was introduced into Europe in 1869 by a priest, Armand David.
Growing conditions of the handkerchief tree
This tree is quite hardy and tolerates temperatures down to -20 °C but nevertheless prefers sheltered locations, as it is sensitive to cold winds and spring frosts. It requires soil that is preferably rich in humus and non-calcareous. It does not grow well in soil that is too compact or soils with stagnant humidity. This species tolerates both full sun and partial shade.
Use
This species is essentially used for its decorative qualities. Its fruit can be eaten when overripe.
Author: Michel Caron
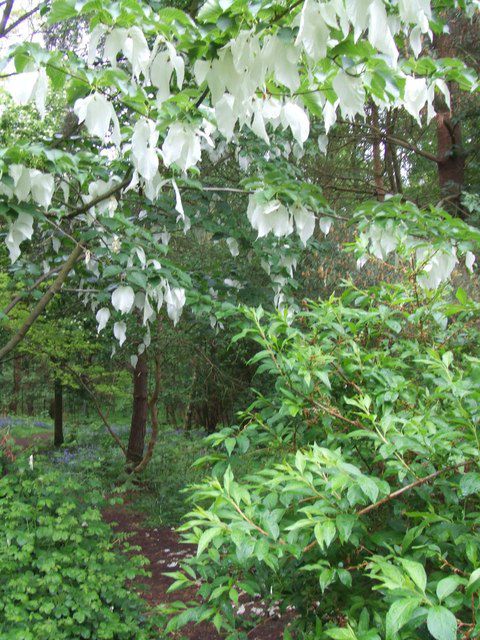 The handkerchief tree is also called the dove tree. © Alice H Myers, Geograph CC by sa 3.0
The handkerchief tree is also called the dove tree. © Alice H Myers, Geograph CC by sa 3.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



