-
 Magnaporthe grisea
Magnaporthe grisea
-
 RNA
RNA
-
 Exocytosis
Exocytosis
-
 Iron-bearing formation
Iron-bearing formation
-
 Emission spectrometry
Emission spectrometry
-
 Pulvillus
Pulvillus
-
 Internet Storm Center
Internet Storm Center
-
 Hashimoto's thyroiditis
Hashimoto's thyroiditis
-
 Deimos
Deimos
-
 Caffeine
Caffeine
-
 Clays (minerals)
Clays (minerals)
-
 Hipparcos
Hipparcos
-
 Olive tree
Olive tree
-
 Lapilli
Lapilli
-
 Hybrid
Hybrid
-
 Malacology
Malacology
-
 El Niño
El Niño
-
 Simplex
Simplex
-
 Collenchyma
Collenchyma
-
 Postulate
Postulate
-
 Handkerchief tree
Handkerchief tree
-
 Calvin cycle
Calvin cycle
-
 Sea ice - Old ice
Sea ice - Old ice
-
 Perseids
Perseids
-
 Dynamo
Dynamo
-
 Laminary
Laminary
-
 CCIR
CCIR
-
 Anopheles
Anopheles
-
 Plagioclasite
Plagioclasite
-
 Incandescent light bulb
Incandescent light bulb
Ginkgo
Ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba) is a magnificent tree, that grows to heights of 25 to 30 metres. A survivor of the many species that used to prosper all around the world at the end of the Cambrian and have since disappeared, it is a true living fossil

Gingko leaf. © Roger B., Flickr CC by nc-sa 3.0
Names
Ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba), a tree from the Ginkgoaceae family, is also called the maidenhair tree.
Botanical description
The male ginkgo has a slender outline, while female trees have a more compact structure. Its lifespan is very long, sometimes exceeding 1,000 years. Its brown and rough bark cracks with age. Its leaves have two plam shaped lobes, and do not have the central vein, thatmost plants have. Its deciduous leaves have a petiole and are located on the branches in small groups reaching 5 to 15 centimetres in length. In autumn, the ginkgo has a magnificent golden yellow foliage. It is a dioecious species, its male inflorescences are greenish, 7-8 centimetre catkins, and its female flowers are bare, with no foral pieces and grouped into pairs. Its fruit look like yellow plums., They are orange-yellow when ripe, and give off a rancid smell.

Ginkgo biloba. © Doblonaut, Flickr by nc-sa 3.0
Origins
Buddhist monks have always venerated this species by planting it near their temples and pagodas in order to prevent fires. Ginkgo is the only living organism that withstood the explosion of the atom bomb dropped on Hiroshima during the Second World War. This tree was introduced into Europe in the 18th century.
Growing conditions
The ginkgo is not very demanding in terms of soil quality. However, it prefers cool siliceous soil or fresh silica-clay soil.
Use
Ginkgoes are found inalong many streets and in parks inof large cities, due to their high resistance to pollution and the ornamental nature of their leaves. Ginkgo is used in medicinal applications especially to cure venous circulation problems.
Author: Michel Caron
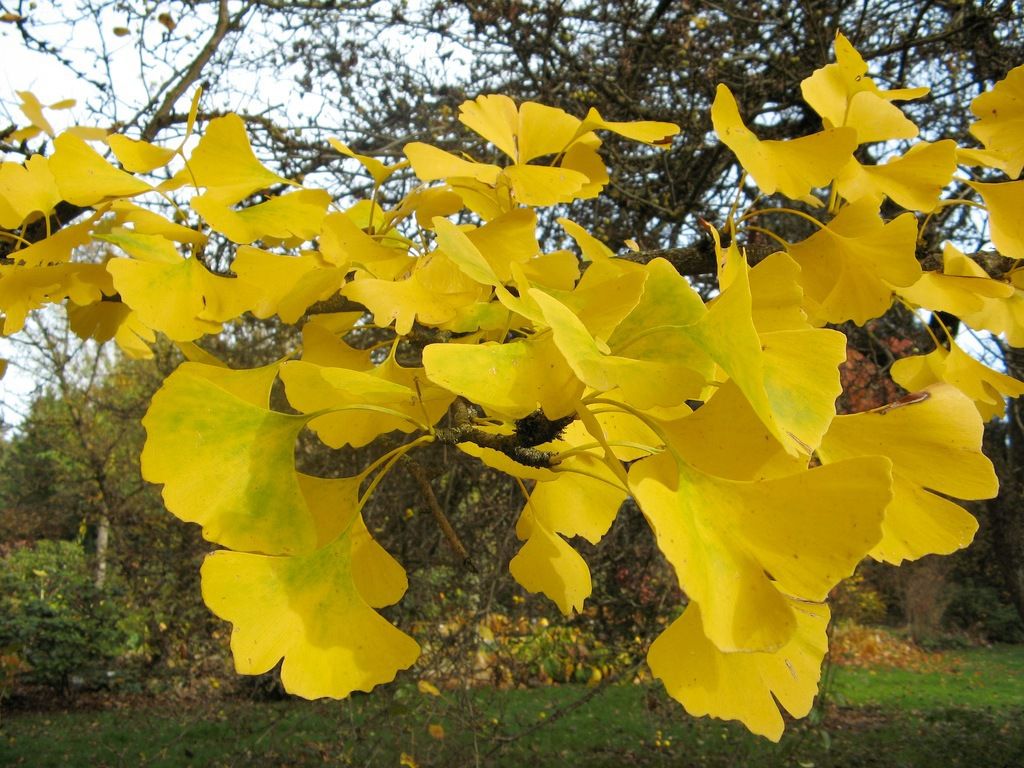 Ginkgo biloba. © Andreasbalzer, Flickr by nc-sa 3.0
Ginkgo biloba. © Andreasbalzer, Flickr by nc-sa 3.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



