-
 Spitzer
Spitzer
-
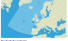 OSPAR Convention
OSPAR Convention
-
 Microglia
Microglia
-
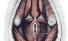 Perineum
Perineum
-
 Hypergolic
Hypergolic
-
 Osterrite
Osterrite
-
 Gruiformes
Gruiformes
-
 Graphics software
Graphics software
-
 DSS
DSS
-
 Bilirubin
Bilirubin
-
 Annular eclipse
Annular eclipse
-
 Atlantic salmon
Atlantic salmon
-
 Numbers
Numbers
-
 Fusiform
Fusiform
-
 Cosmos 1
Cosmos 1
-
 H.264
H.264
-
 Exon
Exon
-
 Granzyme
Granzyme
-
 Touch screen
Touch screen
-
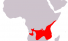 Range
Range
-
 Stamping mill
Stamping mill
-
 Ecological corridor
Ecological corridor
-
 Crust
Crust
-
 Self-signed key
Self-signed key
-
 Deep Space 2
Deep Space 2
-
 Salix viminalis
Salix viminalis
-
 Endergonic
Endergonic
-
 Metastatic
Metastatic
-
 Breadfruit
Breadfruit
-
 Brackish water
Brackish water
Vacuole
A vacuole is a eukaryotic cellular organelle which is specific to plant and fungal cells.
Structure of a vacuole
A vacuole is a large single structure which varies in size depending on the cell and is delineated by a lipid membrane known as a tonoplast. The vacuole makes up 80 to 90% of the volume and weight of the plant cell. It mainly contains water but also organic compounds such as carbohydrates, ions, and pigments, etc.
Role of the vacuole
The main role of the vacuole is to maintain cellular homoeostasis, i.e. maintain correct concentrations of materials in the cytoplasm by selectively storing materials within its membrane.
It also plays an important role in the turgor pressure of plants cells by providing a sufficient pressure inside the cell to maintain the rigidity of specific anatomical structures (stem).
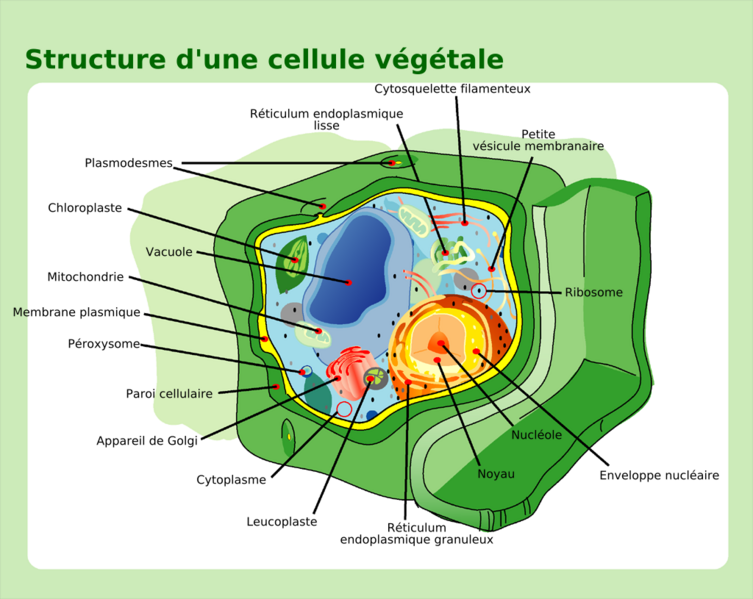 The vacuole is the largest organelle in the plant cell. © Mariana Ruiz Villarreal, Wikimedia, public domain
The vacuole is the largest organelle in the plant cell. © Mariana Ruiz Villarreal, Wikimedia, public domain
Latest
Fill out my online form.



