-
 Endemic stick insect (apterograeffa reunionensis)
Endemic stick insect (apterograeffa reunionensis)
-
 Soyuz / ST
Soyuz / ST
-
 Bunsen Burner
Bunsen Burner
-
 Transcription
Transcription
-
 Lock
Lock
-
 Lime
Lime
-
 Rhesus macaque
Rhesus macaque
-
 Alfvén waves
Alfvén waves
-
 Mangrove swamp
Mangrove swamp
-
 Mimivirus
Mimivirus
-
 Phases of the Moon
Phases of the Moon
-
 Embedding diagram
Embedding diagram
-
 Bursitis
Bursitis
-
 Processor cooling
Processor cooling
-
 One-way hash
One-way hash
-
 Grey matter
Grey matter
-
 Erlang
Erlang
-
 Opt-out
Opt-out
-
 Ocean turbine
Ocean turbine
-
 Heterotrophism
Heterotrophism
-
 Glycolysis
Glycolysis
-
 Magnetic moment
Magnetic moment
-
 Anaesthetic
Anaesthetic
-
 Anatidae
Anatidae
-
 Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria
-
 Archaea
Archaea
-
 Mono-refringence
Mono-refringence
-
 Transit
Transit
-
 Home automation
Home automation
-
 Oesophagus
Oesophagus
Transporter protein
A transporter protein is a protein which crosses both sides of the cell membrane and allows hydrophilic molecules to cross the membrane.
The different types of transport proteins
There are two types of transport proteins: those which facilitate the diffusion of molecules along their electrochemical gradients and those which carry the molecules actively against their electrochemical gradient.
- There are three types of the first group depending on whether or not they transport one or two molecules at the same time and on whether or not the two molecules move in the same direction. These are the uniport, symport and antiport proteins.
- The second group are called active transporters as they only function in the presence of metabolic energy (ATP). They are unable to combat the forces of the electro-chemical gradient without this energy source.
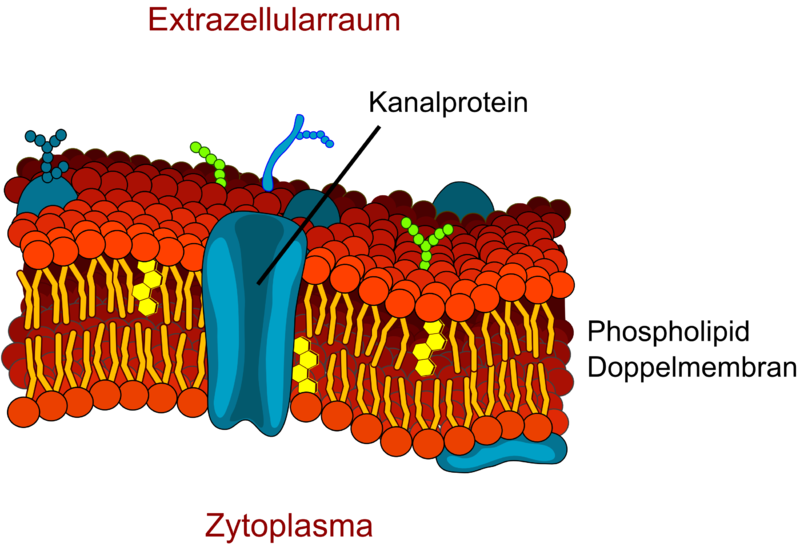 One example of a transporter protein: the canal protein. © LadyofHats, modified by Armin Kübelbeck, Wikimedia CC by 3.0
One example of a transporter protein: the canal protein. © LadyofHats, modified by Armin Kübelbeck, Wikimedia CC by 3.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



