-
 Aubergine
Aubergine
-
 Symmetric algorithm
Symmetric algorithm
-
 Variable star
Variable star
-
 Diplopia
Diplopia
-
 Barium
Barium
-
 Gland
Gland
-
 RPG
RPG
-
 Columbia
Columbia
-
 Supination
Supination
-
 Light pen
Light pen
-
 Triglycerides
Triglycerides
-
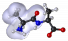 Lipophile
Lipophile
-
 Sea ice - New
Sea ice - New
-
 Argos
Argos
-
 CPU
CPU
-
 Occipital
Occipital
-
 Asian brown cloud
Asian brown cloud
-
 Diagnosis
Diagnosis
-
 Apache
Apache
-
 New Technology Telescope
New Technology Telescope
-
 Botulism
Botulism
-
 Basic rock
Basic rock
-
 Spin
Spin
-
 Denervation
Denervation
-
 e-Couponing
e-Couponing
-
 Vaginal examination
Vaginal examination
-
 Rorqual
Rorqual
-
 Rhesus factor
Rhesus factor
-
 Solar wind
Solar wind
-
 Achromia
Achromia
Thymus
The thymus is an immune system organ located at the base of the neck behind the sternum.
Function of the thymus
The thymus is a primary lymphoid organ, that is, it takes part in the maturation of immune cells, the T lymphocytes.
Prothymocytes mature into T lymphocytes during migration of cells from the cortex to the medulla in response to two hormones produced by the thymus, thymopoietin and thymulin. The lymphocytes then acquire TCR receptors and CD4 and CD8 co-receptors which are involved in antigen recognition. They are the target for positive selection (to confirm that the receptors are appropriate) and negative selection (to confirm that they do not recognise self antigens).
Structure of the thymus
The thymus is composed of two large lobes which atrophy from adolescence The lymphoid tissue gradually gives way to adipose tissue.
The thymus is formed from several lobes which are separated by septa. The peripheral parts are called the cortex (dark) and the internal part is called the medulla (clear).
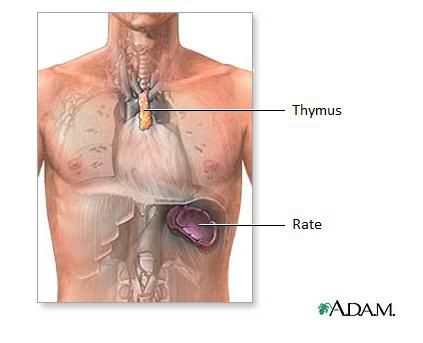 The thymus is the place where T lymphocytes mature. © Adam
The thymus is the place where T lymphocytes mature. © Adam
Latest
Fill out my online form.



