-
 Hysterography
Hysterography
-
 Caterpillar
Caterpillar
-
 Regulator
Regulator
-
 Kuiper belt
Kuiper belt
-
 Angina pectoris
Angina pectoris
-
 CENELEC
CENELEC
-
 Proteome
Proteome
-
 Tethys
Tethys
-
 Curettage
Curettage
-
 Crystalline schist
Crystalline schist
-
 Nicol
Nicol
-
 Flood plain
Flood plain
-
 Jerusalem artichoke
Jerusalem artichoke
-
 Active fault
Active fault
-
 Z0
Z0
-
 Universal time
Universal time
-
 Plateosaurus
Plateosaurus
-
 Astrophysics
Astrophysics
-
 Clinical history
Clinical history
-
 Thale cress
Thale cress
-
 Carpus
Carpus
-
 Calculus
Calculus
-
 IPv6
IPv6
-
 Major axis
Major axis
-
 Magnetometer
Magnetometer
-
 Onco-haematologist
Onco-haematologist
-
 Leukaemia
Leukaemia
-
 Morphing
Morphing
-
 Parallax
Parallax
-
 Oncogene
Oncogene
Testis
The testes are part of the male reproductive system.
Function of the testes
The testes are glands which produce testosterone, the main male hormone responsible for the development of genital organs. It begins to be produced at puberty and triggers changes to transform the boy into a man, by triggering the development of male secondary sexual characteristics.
Spermatogenesis (the production of spermatozoa) also takes place in the testes This begins at puberty and continues throughout the man's life. Whereas girls are therefore born with their entire reserve of eggs, men only begin to produce spermatozoa at puberty. Unlike women, however, men renew their reproductive cell or gamete reserve throughout their lives.
Beginning at puberty, the testes permanently produce new spermatozoa that are carried to the testes through the vas deferens, leave the canal inside the penis, where they mix with a liquid produced by the prostate and seminal vesicles. This fluid and spermatozoa is called "semen". Semen is released by the penis when a man ejaculates. It is expressed by the urethra, which is the channel that carries urine from the bladder outside the body. Each drop of semen contains tens of millions of microscopic spermatozoa. A single spermatozoon reaches the uterus and fertilises the ovum.
Structure of the testes
There are two testes, located alongside the penis outside of the pelvic cavity, in a sac surrounded by a folded skin called the "scrotum". They are directly surrounded by a solid protective connective tissue called the "albuginea". The fact that the testes lie outside of the body reduces their temperature by approximately 2°C compared to body temperature.
Although they vary in size between people, the testes measure an average of 3 x 2 x 5 centimetres, and weigh approximately 18 grams.
The testes are divided into several testicular lobules that contain the seminiferous tubules where spermatogenesis occurs. The spermatozoa ultimately arrive in the epididymal duct where they finish maturing, and they then enter the vas deferens, which is connected to the prostate.
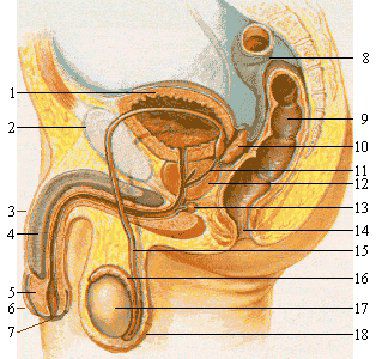 The testes are where spermatozoa are produced. 1. Urine bladder 2. Pubis 3. Penis 4. Corpus cavernosum 5. Glans 6. Prepuce 7. Meatus 8. Sigmoid colon 9. Rectum 10. Seminal vesicle 11. Ejaculatory duct 12. Prostate 13. Cowper's gland 14. Anus 15. Vas deferens 16. Epididymis 17. Testis 18. Scrotum. © BMF81, Wikipedia CC by-sa 3.0
The testes are where spermatozoa are produced. 1. Urine bladder 2. Pubis 3. Penis 4. Corpus cavernosum 5. Glans 6. Prepuce 7. Meatus 8. Sigmoid colon 9. Rectum 10. Seminal vesicle 11. Ejaculatory duct 12. Prostate 13. Cowper's gland 14. Anus 15. Vas deferens 16. Epididymis 17. Testis 18. Scrotum. © BMF81, Wikipedia CC by-sa 3.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



