-
 Quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics
-
 Nutation
Nutation
-
 Antispastic agent
Antispastic agent
-
 SCAR
SCAR
-
 Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis
-
 High energy performance
High energy performance
-
 Pyrrolysine
Pyrrolysine
-
 Hominid
Hominid
-
 Gas giant
Gas giant
-
 Collagen
Collagen
-
 Fratricide
Fratricide
-
 Concussion
Concussion
-
 Metazoan
Metazoan
-
 Proton pump inhibitor
Proton pump inhibitor
-
 Phytohormone
Phytohormone
-
 Vegetarian
Vegetarian
-
 Heuristics
Heuristics
-
 DMB
DMB
-
 Amylase
Amylase
-
 Nuptial plumage
Nuptial plumage
-
 Axial
Axial
-
 DVB-H
DVB-H
-
 Gluten
Gluten
-
 Axion
Axion
-
 NMR
NMR
-
 Balai
Balai
-
 Taurids
Taurids
-
 Spermicide
Spermicide
-
 Fischer-Tropsch process
Fischer-Tropsch process
-
 Artificial CO2 sequestering
Artificial CO2 sequestering
Spinal cord
The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system.
Function of the spinal cord
The spinal cord is the extension of the brain from the cranial vault from the brain stem along the vertebral column in which it is contained. Its role is to distribute nerves from the brain to the different parts of the body.
It is involved in reflexes, such as taking your hand directly away from a burning cooker ring, directly without nerve information passing to the brain.
Structure of the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a white cord approximately 1 cm in diameter and 50 cm long. It has two swellings where the limbs emerge and ends in a point at the second lumbar vertebra. There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves (left and right), which are directly connected to the spinal cord. Each nerve has two nerve roots:
- posterior or sensitive root;
- anterior or motor root.
The spinal nerves are all mixed: motor or sensory.
Two regions are seen on transverse section of the spinal cord:
- Firstly, the grey matter (H shaped) in the centre containing the cell bodies of neurones.
- Secondly, the grey matter in the periphery which contains axons in their myelin sheath.
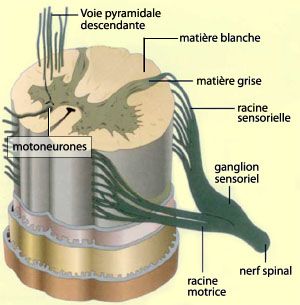
The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system and is an extension of the brain. © psychologie-m-fouchey.psyblogs.net
Latest
Fill out my online form.



