-
 Pinot noir
Pinot noir
-
 Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter
Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter
-
 ActiveX
ActiveX
-
 Brönsted base
Brönsted base
-
 Mandible
Mandible
-
 Cryptography
Cryptography
-
 Ozonosphere
Ozonosphere
-
 Range
Range
-
 Tracheostomy
Tracheostomy
-
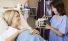 Prostaglandin
Prostaglandin
-
 Vaccine
Vaccine
-
 SIM
SIM
-
 Spyware
Spyware
-
 VIRTIS
VIRTIS
-
 Instrumental aberration
Instrumental aberration
-
 Metal
Metal
-
 Common channel signalling
Common channel signalling
-
 Data stream encryption
Data stream encryption
-
 Peridotite
Peridotite
-
 Acusia
Acusia
-
 Challenger
Challenger
-
 Meteorite
Meteorite
-
 Tornado
Tornado
-
 Follicle
Follicle
-
 Sunyaev-Zel'dovich effect
Sunyaev-Zel'dovich effect
-
 Blastocyst
Blastocyst
-
 Moho
Moho
-
 Tongue
Tongue
-
 Old karst
Old karst
-
 Malware
Malware
Selenocysteine
Selenocysteine (Sec or U) is a rare amino acid which is present in some enzymes.
Structure of selenocysteine
As with all amino acids, selenocysteine is composed of a COOH group and an NH2group which are involved in peptide bonds. Its side chain contains an atom of selenium: CH2-SeH.
Function of selenocysteine
There is no free selenocysteine in the cell. Selenocysteine is produced from serine, which has previously been bound to a specific transfer RNA whose anti codon pairs with the UGA codon of the messenger RNA.
This codon is usually a stop codon which causes arrest in protein synthesis when it is read by the ribosome. A specific mechanism involving proteins and a loop and stem on the messenger RNA leaves a place where selenocysteine can be incorporated.
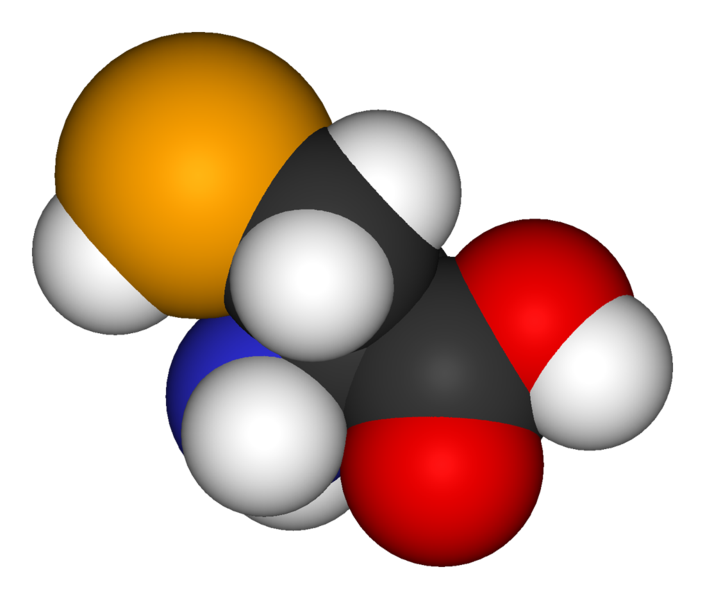 Selenocysteine is a rare amino acid which incorporates at a stop codon. © Public domain
Selenocysteine is a rare amino acid which incorporates at a stop codon. © Public domain
Latest
Fill out my online form.



