-
 Proteolysis
Proteolysis
-
 Contrast
Contrast
-
 Pneumatophore
Pneumatophore
-
 Acromegaly
Acromegaly
-
 DCE
DCE
-
 Emetic
Emetic
-
 Barium
Barium
-
 Southwest European nase
Southwest European nase
-
 Essential oil
Essential oil
-
 Artesian well
Artesian well
-
 Aristolochia
Aristolochia
-
 Gastroscopy
Gastroscopy
-
 Vitamin E
Vitamin E
-
 SNAPI
SNAPI
-
 Arytenoid
Arytenoid
-
 Pelagic
Pelagic
-
 Grape
Grape
-
 Electronic configuration
Electronic configuration
-
 Lyman-alpha forest
Lyman-alpha forest
-
 Blue Motion
Blue Motion
-
 Saprophage
Saprophage
-
 Lidar
Lidar
-
 Athetosis
Athetosis
-
 Conveyor belt
Conveyor belt
-
 Optimum pH
Optimum pH
-
 Wind turbine
Wind turbine
-
 Greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gas
-
 Kjokkenmodding
Kjokkenmodding
-
 Sweet chestnut
Sweet chestnut
-
 Solar eclipse of 11 August 1999
Solar eclipse of 11 August 1999
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (or brewer's yeast, baker's yeast) is a model organism studied in biology laboratories.
Classification of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a unicellular yeast, a eukaryotic organism belonging to the fungal kingdom and the Saccharomycetes family.
Characteristics of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a round or oval cell, 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter. It has a linear double stranded DNA genome containing 13 million base pairs divided into 16 chromosomes (which have been completely sequenced). It replicates fairly quickly, approximately every two hours at 30°C. It can live in different environments:
- in an aerobic environment in the presence of oxygen where it reproduces rapidly through a respiration process;
- in an aerobic environment where it ferments, i.e.it converts sugar into alcohol. It is a widely used yeast in cooking (to raise dough) and to produce alcohol.
Use of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the laboratory
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a model organism in that it is the simplest eukaryotic organism. Researchers can therefore try to understand the processes involved in biological mechanisms before testing in human beings. It has the advantage of reproducing rapidly and can also be transformed in order to express new genes and test substances, etc.
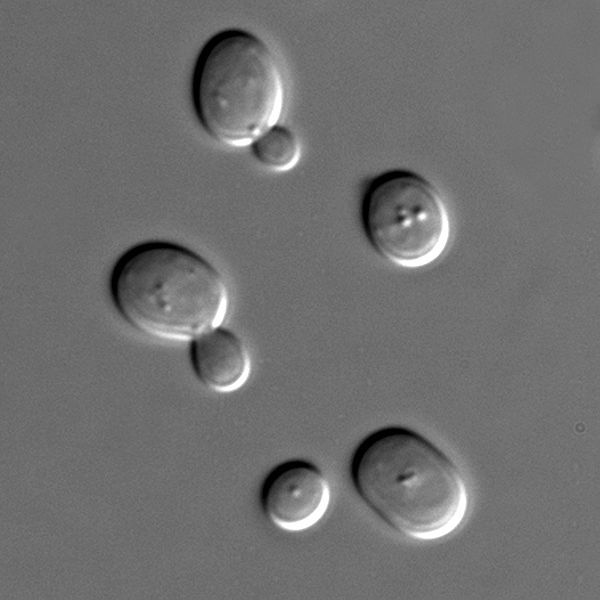 The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a model organism used to study eukaryotes overall. © Masur, Wikimedia, public domain
The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a model organism used to study eukaryotes overall. © Masur, Wikimedia, public domain
Latest
Fill out my online form.



