-
 Vertex
Vertex
-
 Eccentric anomaly
Eccentric anomaly
-
 Transmission electron microscope
Transmission electron microscope
-
 Dormitory
Dormitory
-
 Pervasive environment
Pervasive environment
-
 Anticyclonic circulation
Anticyclonic circulation
-
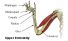 Humerus
Humerus
-
 Measles virus
Measles virus
-
 Combined pill
Combined pill
-
 Astronomical coordinates
Astronomical coordinates
-
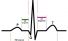 Electrocardiogram
Electrocardiogram
-
 Arteriosclerosis
Arteriosclerosis
-
 Ria
Ria
-
 Chicxulub
Chicxulub
-
 Mesostase
Mesostase
-
 Local group
Local group
-
 Palomares nuclear incident
Palomares nuclear incident
-
 Astrometric direction
Astrometric direction
-
 Aponeurosis
Aponeurosis
-
 Biome
Biome
-
 First law of thermodynamics
First law of thermodynamics
-
 Hardness
Hardness
-
 Clementine
Clementine
-
 Aleppo pine
Aleppo pine
-
 Hirudinea
Hirudinea
-
 Force couple
Force couple
-
 Monospecific
Monospecific
-
 SOHO
SOHO
-
 Pressure ulcer
Pressure ulcer
-
 IPv6
IPv6
RNA polymerase
An RNA polymerase is an enzyme which synthesises (or polymerises) RNA molecules by copying the DNA (in which case we refer to DNA-dependent RNA polymerase) or by copying the RNA (in which case we refer to RNA-dependent polymerase).
Function of RNA polymerases
Whilst prokaryotes have only one RNA polymerase, eukaryotes (including human beings) have three enzymes which can synthesise RNA. They are large enzyme complexes composed of several protein chains. They all have sites which can recognise and attach to certainDNAsequences, recruit the necessary nucleotides to extend the chain, and catalyse the formation of the nuclear bond (phosphodiester bond).
Structure of RNA polymerases
Bacterial and Archaeal RNA polymerase can synthesise all of the cell's RNA. On the other hand, the different eukaryotic RNA polymerases have quite distinct roles.
- Pol I RNA synthesises ribosomal RNA;
- Pol II RNA synthesises messenger RNA, the precursors of proteins ;
- Pol III RNA synthesises transfer RNA and 5S ribosomal RNA.
Other RNA polymerases (IV and V) are currently being studied and appear to be involved in the RNA interference mechanism.
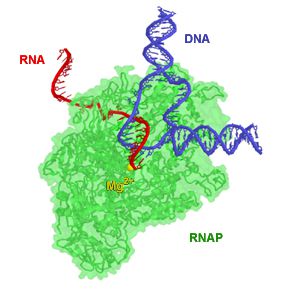
RNA polymerases synthesise the strands of RNA (in red) usually from DNA (in blue). © Abbondanzieri, Wikimedia, public domain
Latest
Fill out my online form.



