-
 Gruiformes
Gruiformes
-
 Natural selection
Natural selection
-
 Substitution deposit
Substitution deposit
-
 Sea ice
Sea ice
-
 Gel
Gel
-
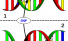 SNP
SNP
-
 Solfatare
Solfatare
-
 Cave
Cave
-
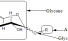 Oside
Oside
-
 Trap
Trap
-
 Malware
Malware
-
 Cyst
Cyst
-
 FDD
FDD
-
 Feldspars
Feldspars
-
 Moisture regime
Moisture regime
-
 Mono-refringence
Mono-refringence
-
 Fumaroles
Fumaroles
-
 Pterophile
Pterophile
-
 Crest
Crest
-
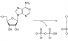 Lyase
Lyase
-
 Chondroma
Chondroma
-
 Giotto
Giotto
-
 Coralloid
Coralloid
-
 Oxidation
Oxidation
-
 Ganymede
Ganymede
-
 Artificial meadow
Artificial meadow
-
 Retina
Retina
-
 Dinosaur
Dinosaur
-
 Homologous chromosomes
Homologous chromosomes
-
 Tungsten
Tungsten
Renaturation
Renaturation of a protein is the opposite of the phenomenon of denaturation: when the medium containing a protein returns to its normal conditions (pH, temperature, etc.), the denatured protein returns to its initial conformation.
Under these conditions, the binding between the protein molecules is restored and all of the polypeptide chains return spontaneously to their three-dimensional structures (secondary and tertiary structures).
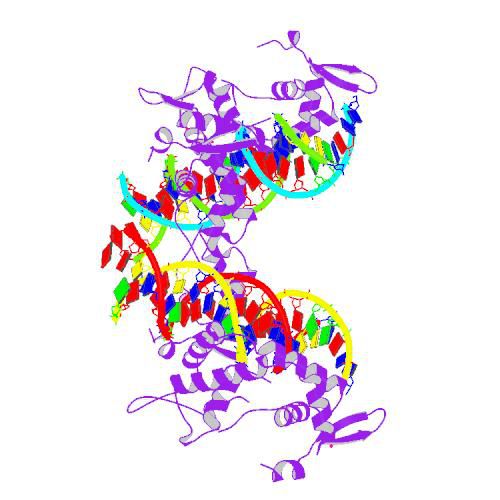 Renaturation of a protein allows it to return to its three-dimensional conformation. © PDB, Wikimedia public domain
Renaturation of a protein allows it to return to its three-dimensional conformation. © PDB, Wikimedia public domain
Latest
Fill out my online form.



