-
 Recovery
Recovery
-
 Resection
Resection
-
 Incense cedar
Incense cedar
-
 Chelicerae
Chelicerae
-
 Surfactant
Surfactant
-
 Mesothermal deposit
Mesothermal deposit
-
 Pleochroism
Pleochroism
-
 Gram negative bacterium
Gram negative bacterium
-
 Sundancer
Sundancer
-
 Acidosis
Acidosis
-
 The Dumbbell nebula
The Dumbbell nebula
-
 Cytokine
Cytokine
-
 FPS
FPS
-
 Homo ergaster
Homo ergaster
-
 IP
IP
-
 GMO
GMO
-
 AES
AES
-
 Extruded polystyrene
Extruded polystyrene
-
 Clostridium botulinum
Clostridium botulinum
-
 Frequency
Frequency
-
 Log in
Log in
-
 Ovariectomy
Ovariectomy
-
 Clay
Clay
-
 Crystal form
Crystal form
-
 Inlandsis
Inlandsis
-
 Lactitol
Lactitol
-
 UTR
UTR
-
 SECAM
SECAM
-
 Anthrax
Anthrax
-
 Cosmos 1
Cosmos 1
Pyruvate
Pyruvate is the anionic form of pyruvic acid. It is also a major biological molecule.
Structure of pyruvate
Pyruvate is a α-keto-acid with the structure CH3-CO-COOH, which has a carboxylic acid (COOH) group and ketone group.
Function of pyruvate
Pyruvate is a metabolite involved in a large number of biological processes:
- Firstly, the Krebs cycle: pyruvate is decarboxylated by a multi-enzyme complex into acetyl-coenzyme A, a molecule involved in the first stage of the Krebs cycle;
- Secondly, glycolysis: pyruvate is the final product of glycolysis (two pyruvate molecules are formed from a glucose molecule). Thridly, they are obtained from the dephosphorylation of PEP (phosphoenolpyruvate) and transfer phosphate to an ADP molecule to form an ADP molecule.
- Lastly, gluconeogenesis: pyruvate is converted into oxaloacetate by pyruvate carboxylase.
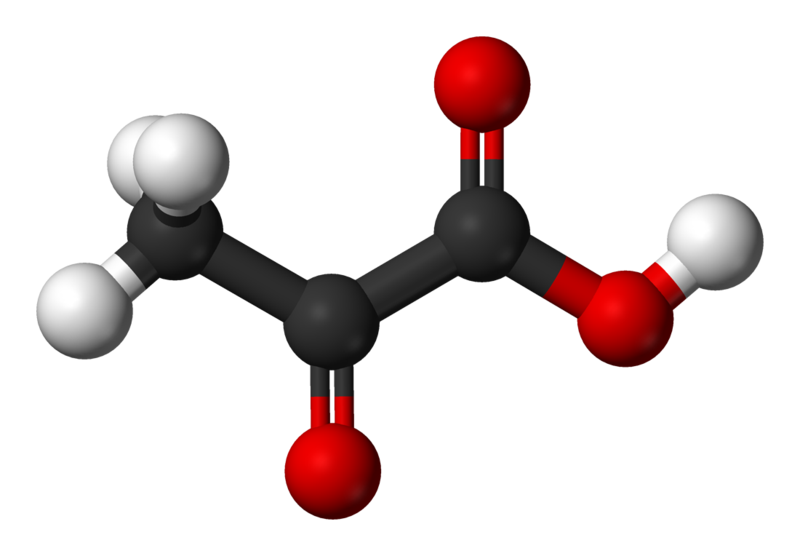 Pyruvate is the ionised form of pyruvic acid. © Benjah-bmm27, Wikimedia, public domain
Pyruvate is the ionised form of pyruvic acid. © Benjah-bmm27, Wikimedia, public domain
Latest
Fill out my online form.



