-
 Epiphysis
Epiphysis
-
 Pioneer species
Pioneer species
-
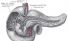 Exocrine gland
Exocrine gland
-
 Monogyny
Monogyny
-
 Scintigraphy
Scintigraphy
-
 Rydberg atom
Rydberg atom
-
 Bifurcation
Bifurcation
-
 Growth twin
Growth twin
-
 Transgene
Transgene
-
 Antimetabolite
Antimetabolite
-
 Conventional cytotoxic medicine
Conventional cytotoxic medicine
-
 MMB
MMB
-
 Fermentation
Fermentation
-
 Channelrhodopsin
Channelrhodopsin
-
 Chromatic aberration
Chromatic aberration
-
 Ferralisation
Ferralisation
-
 Silicosis
Silicosis
-
 Fovea
Fovea
-
 X9.17
X9.17
-
 Apomixis
Apomixis
-
 Oedema
Oedema
-
 Urban heat island
Urban heat island
-
 Sputnik
Sputnik
-
 API
API
-
 Translucent
Translucent
-
 M86
M86
-
 Bunsen Burner
Bunsen Burner
-
 Diplegia
Diplegia
-
 Lepidoptera
Lepidoptera
-
 Carpus
Carpus
Protein
Proteins are biological molecules which can have a very wide range of activities.
Role of proteins
Proteins carry a very wide range of functions within the cell or body.
They may play:
- a structural role (such as actin or tubulin contributing to the architecture of the cell, keratin which makes up hair ;
- an enzymatic role (such as DNA polymerase which recopies DNA) ;
- a hormonal role (such as insulin, which regulated blood glucose concentrations) ;
- a motor role (such as myosin, which transports molecules in the cell)…
Production of proteins
Proteins are coded for by genes and synthesised by ribosome during the process of RNA translation They are created by successive incorporation of amino acids, held together by peptide bonds in the order dictated by the succession of codons on the RNA.
Protein structure
Depending on their amino acid order and the binding between them, proteins take on particular conformations which are essential for them to function. Some structures are very commonly seen :
- the alpha helices, in which the amino acids form a helix through hydrogen bonds between each other;
- the beta sheets, where hydrogen bonds between the amino acids promote the formation of superimposed layers.
Post-translational chemical modifications can also contribute to their function (acetylations, phosphorylations, disulphide bridges...).
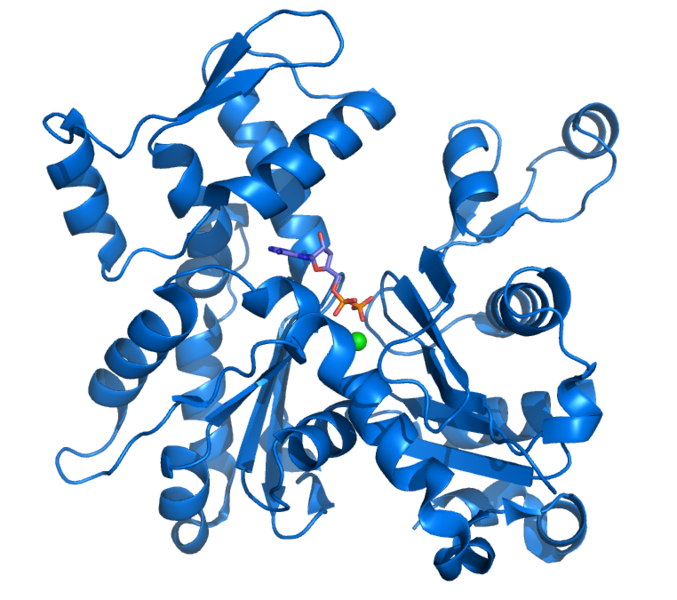 Actin is a protein with a three-dimensional structure made up of alpha helices (corkscrews) and beta sheets (arrows). © Thomas Splettstoesser, Wikimedia, CC by-sa 3.0
Actin is a protein with a three-dimensional structure made up of alpha helices (corkscrews) and beta sheets (arrows). © Thomas Splettstoesser, Wikimedia, CC by-sa 3.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



