-
 Allotransplantation
Allotransplantation
-
 Oberon
Oberon
-
 Ibuprofen
Ibuprofen
-
 Menstrual cycle
Menstrual cycle
-
 Pay per view
Pay per view
-
 Differentiation
Differentiation
-
 Water Framework Directive
Water Framework Directive
-
 International Nuclear Event Scale
International Nuclear Event Scale
-
 Crab nebula
Crab nebula
-
 GFP
GFP
-
 Monosaccharides
Monosaccharides
-
 Feral
Feral
-
 Yohkoh
Yohkoh
-
 GPS
GPS
-
 Lepidoptera
Lepidoptera
-
 Progestogen
Progestogen
-
 Fluorite
Fluorite
-
 Immune complex
Immune complex
-
 Ketose
Ketose
-
 Constellation of Taurus
Constellation of Taurus
-
 Mineral water
Mineral water
-
 Magnesiowüstite
Magnesiowüstite
-
 Incense cedar
Incense cedar
-
 Counter-Strike
Counter-Strike
-
 ICT
ICT
-
 Vertebral column
Vertebral column
-
 Action potential
Action potential
-
 S-Video
S-Video
-
 Beta cells
Beta cells
-
 Subspecies
Subspecies
Polyprotein
A polyprotein (which etymologically means "several proteins") is the product of a single gene as a single protein which is usually non-functional.
The polyprotein is then cleaved at specific sites into smaller proteins by one or more proteases. When they are separated from each other the proteins can then perform their function.
This synthesis strategy for proteins is used by different viruses (Hepatitis C, Poliovirus...)
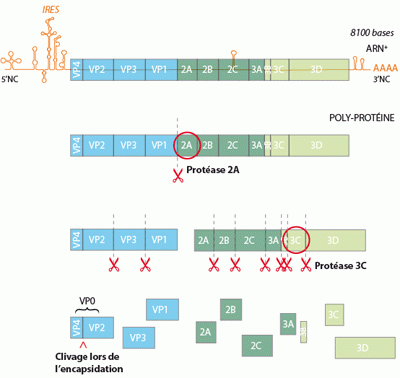 The Poliovirus polyprotein is firstly cleaved by protease 2A, and then by protease 3C, leading to around ten smaller proteins. © UCL / Licence Creative Commons
The Poliovirus polyprotein is firstly cleaved by protease 2A, and then by protease 3C, leading to around ten smaller proteins. © UCL / Licence Creative Commons
Latest
Fill out my online form.



