-
 Forced circulation
Forced circulation
-
 CRBPO / Centre for Research in Biology and Bird Population
CRBPO / Centre for Research in Biology and Bird Population
-
 Club of Rome
Club of Rome
-
 Oceanic mixed layer
Oceanic mixed layer
-
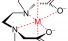 Chelation
Chelation
-
 CPU
CPU
-
 Microfiltration
Microfiltration
-
 Chlamydia infection
Chlamydia infection
-
 DTS
DTS
-
 Defensin
Defensin
-
 Skype
Skype
-
 Welding
Welding
-
 Statin
Statin
-
 Thymus
Thymus
-
 Videoconference
Videoconference
-
 Encephalon
Encephalon
-
 Triangle galaxy
Triangle galaxy
-
 Tadpole
Tadpole
-
 Epidermis
Epidermis
-
 Staples
Staples
-
 Ammonia
Ammonia
-
 Cranial vault
Cranial vault
-
 Ebola virus haemorrhagic fever
Ebola virus haemorrhagic fever
-
 Tethys
Tethys
-
 OSD
OSD
-
 Gram positive bacterium
Gram positive bacterium
-
 Half-life
Half-life
-
 Wood energy
Wood energy
-
 Point-to-point link
Point-to-point link
-
 Microprocessor
Microprocessor
Pituitary gland
The pituitary gland is part of the central nervous system.
Function of the pituitary gland
The pituitary gland is an endocrine gland located in the brain, which responds to stimuli from the hypothalamus, producing specific hormones which are released into the blood:
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH);
- thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), which stimulates the secretion of thyroid hormones;
- somatotropin (GH) which stimulates cell growth;
- prolactin (PRL), which stimulates milk production;
- gonadotrophins (sex hormones), lutenising hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH);
- endorphins, molecules giving a sense of well-being;
- melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) which stimulates production of melanin.
Structure of the pituitary gland
The pituitary gland is a gland the size of a pea weighing 0.5 grams and connected to the hypothalamus by a stem known as the pituitary gland stalk. The pituitary gland is divided into two lobes:
- The anterior pituitary gland (adenohypophysis) in front;
- the posterior pituitary gland (neurohypophysis) behind.
The posterior pituitary gland is a projection of the hypothalamus which stores and releases ocytocin and vasopressin.
Different cell types produce each of these hormones.
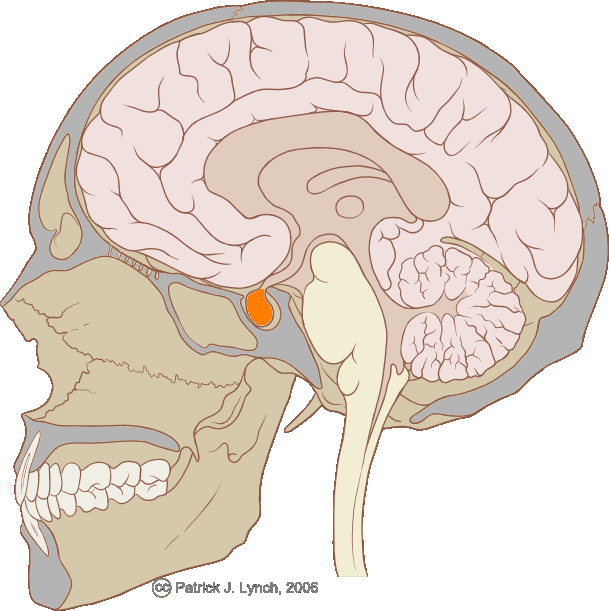 The pituitary gland is an endocrine gland that controls various biological functions. The pituitary gland is located in the middle of the brain and is closely connected to the hypothalamus. © Patrick J. Lynch / Licence Creative Commons
The pituitary gland is an endocrine gland that controls various biological functions. The pituitary gland is located in the middle of the brain and is closely connected to the hypothalamus. © Patrick J. Lynch / Licence Creative Commons
Latest
Fill out my online form.



