-
 Scintigraphy
Scintigraphy
-
 Digestive enzyme
Digestive enzyme
-
 Sclerotin
Sclerotin
-
 Grained rock
Grained rock
-
 Albumin
Albumin
-
 Oxidation zone
Oxidation zone
-
 Guanase
Guanase
-
 Cartilage
Cartilage
-
 Nocturnal
Nocturnal
-
 Packet switching
Packet switching
-
 Colostrum
Colostrum
-
 AMR
AMR
-
 Pervasive environment
Pervasive environment
-
 NIAID
NIAID
-
 Arthropod
Arthropod
-
 Endoprosthesis
Endoprosthesis
-
 Plutonium
Plutonium
-
 Friction
Friction
-
 Pomegranate
Pomegranate
-
 Marcescence
Marcescence
-
 Haemolysis
Haemolysis
-
 Bubo
Bubo
-
 Winter solstice
Winter solstice
-
 Lymph
Lymph
-
 GSS-API
GSS-API
-
 Elytra
Elytra
-
 Educational software
Educational software
-
 Ependymoma
Ependymoma
-
 Yohkoh
Yohkoh
-
 ESO
ESO
Larynx
The larynx belongs to the respiratory system.
Function of the larynx
The larynx is an organ located in the throat between the pharynx and trachea. Its main role is to allow air to pass into the lungs during inspiration or to the exterior during expiration.
It also contains a membrane which closes automatically when food passes from the pharynx into the oesophagus during swallowing, thus preventing foods from reaching the respiratory tract (for example, the trachea).
The larynx also plays an important role in speech. It contains the vocal cords and muscles that change the opening of the lumen of the larynx consequently changing the sounds that are produced.
Structure of the larynx
The larynx is an osteo-cartilaginous conduit which is divided into three parts:
- the vestibule (superior larynx or supraglottic larynx),
- the glottic larynx (middle);
- and the infraglottic larynx (inferior).
The hyoid bone is connected to the upper part but is not considered to be part of the larynx
The different cartilages (thyroid, cricoid, arytenoid, epiglottis) are connected by ligaments and form the outline which is known as the Adam's apple. The cartilages are covered by laryngeal muscles, which allow the larynx to move, and by a mucosa, which is similar to the mucosa in the trachea.
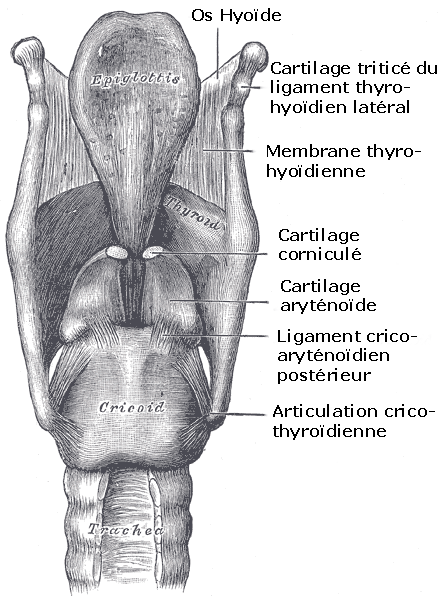 The larynx is a cartilaginous structure which opens into the respiratory system. © Wikimedia Commons
The larynx is a cartilaginous structure which opens into the respiratory system. © Wikimedia Commons
Latest
Fill out my online form.



