-
 Diatomite
Diatomite
-
 Influenza virus
Influenza virus
-
 Giant star
Giant star
-
 Thrombocyte
Thrombocyte
-
 Aposematism
Aposematism
-
 Ependymoma
Ependymoma
-
 Polymetallic
Polymetallic
-
 Desert pavement or reg
Desert pavement or reg
-
 Magnetar
Magnetar
-
 Ketose
Ketose
-
 Caenorhabditis elegans
Caenorhabditis elegans
-
 Antidepressant
Antidepressant
-
 Pneumatolytic
Pneumatolytic
-
 Diaclase
Diaclase
-
 Continental slope
Continental slope
-
 Anabolism
Anabolism
-
 Exocytosis
Exocytosis
-
 Crude oil
Crude oil
-
 Atom
Atom
-
 Ecotoxicology
Ecotoxicology
-
 Inconel
Inconel
-
 Umbilical cord
Umbilical cord
-
 Tempel 1 comet
Tempel 1 comet
-
 Ammon's horn
Ammon's horn
-
 Sialidase
Sialidase
-
 Smart phone
Smart phone
-
 Backdoor
Backdoor
-
 Columbia
Columbia
-
 Inflorescence
Inflorescence
-
 Osteoclast
Osteoclast
Factor IX
Factor IX is also called Christmas factor or antihaemophilia B factor and is one of the essential components in blood coagulation. The protein is coded for by gene F9 and is found in an inactive state in the blood circulation. When a vessel is damaged, foreign bodies infiltrate. As soon as factor IX comes into contact with one of these it activates and enables the production of an enzyme, thrombokinase, which is then involved in the coagulation reactions leading to formation of a blood clot.
If this factor IX is absent, people suffer from haemophilia B.
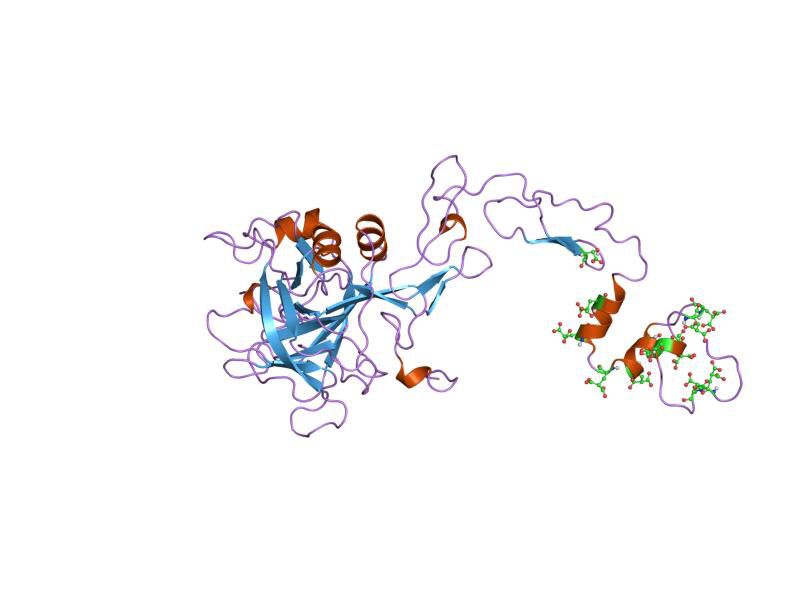 Three-dimensional structure of factor IX. © Jawahar Swaminathan et EBI, Wikipedia, DP
Three-dimensional structure of factor IX. © Jawahar Swaminathan et EBI, Wikipedia, DP
Latest
Fill out my online form.



