-
 Convulsion
Convulsion
-
 M48
M48
-
 Spectrometry
Spectrometry
-
 Fog
Fog
-
 Complex
Complex
-
 Asteroid belt
Asteroid belt
-
 CET Time
CET Time
-
 Quake
Quake
-
 Chromatid
Chromatid
-
 Electrolysis
Electrolysis
-
 Digiscoping
Digiscoping
-
 Mucosa
Mucosa
-
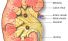 Kidney
Kidney
-
 Continental rift
Continental rift
-
 Scart
Scart
-
 Floppy disk
Floppy disk
-
 Pliocene
Pliocene
-
 Microglia
Microglia
-
 Nicolaier bacillus
Nicolaier bacillus
-
 Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis
-
 Pumice
Pumice
-
 Non-opiate analgesic
Non-opiate analgesic
-
 Bunsen Burner
Bunsen Burner
-
 Placode
Placode
-
 EMS
EMS
-
 Monsoon
Monsoon
-
 Radish
Radish
-
 Focal epilepsy
Focal epilepsy
-
 Ares I
Ares I
-
 Venera
Venera
DNA ligase
A DNA ligase is an enzyme which can repair DNA by creating new covalent bonds between two pieces ofDNA.
Structure of DNA ligases
Like all enzymes, the DNA ligases are proteins with an active site enabling the enzymatic reaction and a donor (a nucleotide OH group) and acceptor (a phosphate group from another nucleotide) molecular recognition sites which make the reaction specific.
Function of DNA ligases
The role of the DNA ligases is to covalently bind two pieces of DNA together. Using a molecule of DNA that provides them with the necessary energy, the DNA ligases create a phosphodiester bond between two nucleotides, whether these belong to a single stranded or a double stranded DNA.
There are different type of DNA ligases which have roles in different biological process:
- DNA ligase 1 is involved in DNA replication when the new strands produced (the Okasaki fragments) must be connected together.
- The other types of DNA ligases (2, 3, or 4) are involved in the repair of DNA breaks.
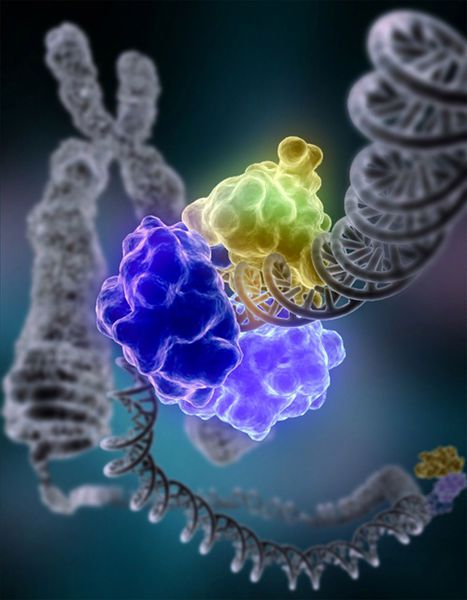 DNA ligase repairs DNA. © Courtesy of Tom Ellenberger, Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
DNA ligase repairs DNA. © Courtesy of Tom Ellenberger, Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
Latest
Fill out my online form.



