-
 Pteridophyte
Pteridophyte
-
 Jilin petrochemical plant disaster
Jilin petrochemical plant disaster
-
 Claudication
Claudication
-
 Decarboxylation
Decarboxylation
-
 Cement
Cement
-
 Ghost lineage
Ghost lineage
-
 The theory of punctuated equilibrium
The theory of punctuated equilibrium
-
 Sea ice - Old ice
Sea ice - Old ice
-
 Birefringence
Birefringence
-
 Hemolymph
Hemolymph
-
 Mediterranean diet
Mediterranean diet
-
 Encryption
Encryption
-
 Brightening
Brightening
-
 Sun-synchronous
Sun-synchronous
-
 Launch campaign
Launch campaign
-
 M 66
M 66
-
 Endocrine
Endocrine
-
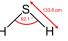 Hydrogen sulphide
Hydrogen sulphide
-
 Axillary
Axillary
-
 SPOT 5
SPOT 5
-
 Photolysis
Photolysis
-
 Porphyroblast
Porphyroblast
-
 Hybrid vehicle
Hybrid vehicle
-
 Androsterone
Androsterone
-
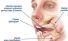 Salivary gland
Salivary gland
-
 Geode
Geode
-
 REACH
REACH
-
 Interferon
Interferon
-
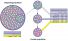 Genetic drift
Genetic drift
-
 Macromolecule
Macromolecule
Centriole
The centriole is a specific part of animal cells.
Structure of the centriole
The centriole is a hollow cylindrical structure containing nine triplets of microtubules surrounded by many other proteins. A centriole is occasionally bound perpendicular to a second centriole to form a centrosome.
Function of the centriole
The centriole is the starting point for polymerisation of tubular proteins to form microtubules (cytoskeleton). The centrioles are therefore found at the base of cilia and flagelli where microtubules are important due to their shape.
Centrioles are also involved (in the form of a centrosome) in the formation of mitotic spindles during cell division.
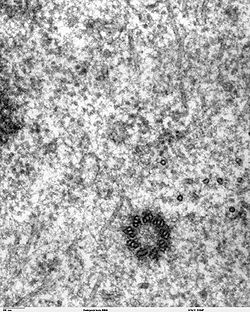
The centriole is a structure composed of nine triplets of microtubules. © Louisa Howard, Miguel Marin-Padilla, Wikimedia, public domain
Latest
Fill out my online form.



