-
 Electromyogram
Electromyogram
-
 Randomised study
Randomised study
-
 GSS-API
GSS-API
-
 Transgenesis
Transgenesis
-
 Wavelength
Wavelength
-
 Space-time
Space-time
-
 Coprocessor
Coprocessor
-
 Hydromorphy
Hydromorphy
-
 Hybrid hard drive
Hybrid hard drive
-
 Gliding
Gliding
-
 Hardness
Hardness
-
 Interdisciplinarity
Interdisciplinarity
-
 Allosome
Allosome
-
 Einstein's box
Einstein's box
-
 Fine particle
Fine particle
-
 Blood-brain barrier
Blood-brain barrier
-
 Crest
Crest
-
 Hypothesis
Hypothesis
-
 Impregnation
Impregnation
-
 Virtual universe
Virtual universe
-
 Elongated facies
Elongated facies
-
 CPU
CPU
-
 Cryogenian
Cryogenian
-
 Oviparous
Oviparous
-
 Cryogenic
Cryogenic
-
 Polysaccharide
Polysaccharide
-
 Kiosk
Kiosk
-
 Vector processor
Vector processor
-
 Ardipithecus
Ardipithecus
-
 CDK
CDK
Aspartic acid
Aspartic acid (Asp, D or aspartate) is one of the 22 amino acids found in proteins.
Structure of aspartic acid
Like all the amino acids, aspartic acid has two functional groups: a carboxyl group (COOH) and an amine group (NH2). It has the following side chain: -CH2-COOH.
Aspartic acid is polar and dicarboxylic, making it the most acid of the amino acids.
Function of aspartic acid
Aspartic acid is not an essential amino acid, as it can be made by the body from oxaloacetate.
It is a urea cycle metabolite and is involved in gluconeogenesis and in the production of inosine, a nitrogen base precursor.
Aspartic acid is also a neuromediator which is less potent than glutamate.
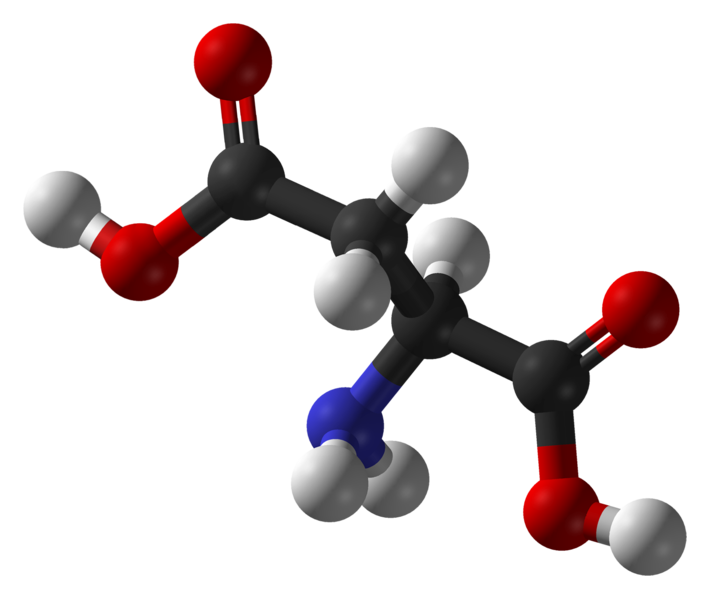 Aspartic acid is an acid amino acid (the carbon atom is shown in black, the oxygen in red, nitrogen in blue, and hydrogen in white). © Ben Mills, public domain
Aspartic acid is an acid amino acid (the carbon atom is shown in black, the oxygen in red, nitrogen in blue, and hydrogen in white). © Ben Mills, public domain
Latest
Fill out my online form.



