-
 Accretion disk
Accretion disk
-
 EUCEB
EUCEB
-
 TDD
TDD
-
 Therapy
Therapy
-
 Limescale
Limescale
-
 Atom
Atom
-
 Crenellation
Crenellation
-
 Galileo
Galileo
-
 Fertilisation
Fertilisation
-
 Maculopapular rash
Maculopapular rash
-
 Solid solution
Solid solution
-
 Medical team
Medical team
-
 Biot-Savart law
Biot-Savart law
-
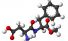 Aspartame
Aspartame
-
 Constellation of Taurus
Constellation of Taurus
-
 Endosome
Endosome
-
 Antidepressant
Antidepressant
-
 Post-mortem lividity
Post-mortem lividity
-
 Polar bear
Polar bear
-
 GNSS
GNSS
-
 Progestogen pill
Progestogen pill
-
 DVD audio
DVD audio
-
 Antiviral
Antiviral
-
 Neutrophile
Neutrophile
-
 Coal
Coal
-
 Phycocyanin
Phycocyanin
-
 Planck constant
Planck constant
-
 Plasma membrane
Plasma membrane
-
 Diuresis
Diuresis
-
 Abiotic
Abiotic
Asparagine
Asparagine (Asn or N) is one of the 22 amino acids contained in proteins. It was the first amino acid discovered, in asparagus, hence its name.
Structure of asparagine
Like all amino acids, asparagine has two functional groups, a carboxyl group (COOH) and an amine group (NH2). It has the following side chain: -CH2-CO-NH2. Asparagine is a polar, uncharged, hydrophilic amino acid.
Function of asparagine
Asparagine is not an essential amino acid as it can be produced in the body from oxaloacetate.
Asparagine is used in the biosynthesis of ammonia and is involved in the correct functioning of neurones.
A reaction between asparagine and sugars at high temperature produces acrylamide, a carcinogen responsible for the grilled taste of food.
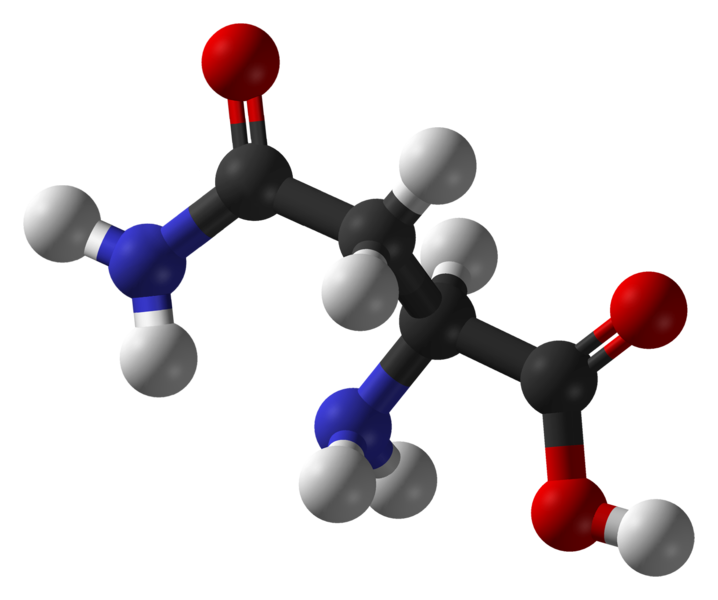 Asparagine is a polar amino acid (carbon in black, oxygen in red, nitrogen in blue and hydrogen in white). © Ben Mills, public domain
Asparagine is a polar amino acid (carbon in black, oxygen in red, nitrogen in blue and hydrogen in white). © Ben Mills, public domain
Latest
Fill out my online form.



